Periodontal disease
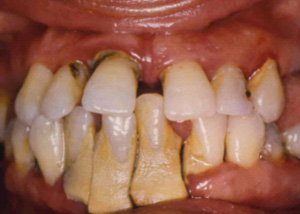 The term Periodontal Disease identifies an oral inflammatory disease affecting periodontal, the supporting structure of the tooth. The disease manifests itself initially as an inflammation of the marginal gingiva that, if neglected, chronic, slowly evolving into periodontitis, better known as periodontal disease.
The term Periodontal Disease identifies an oral inflammatory disease affecting periodontal, the supporting structure of the tooth. The disease manifests itself initially as an inflammation of the marginal gingiva that, if neglected, chronic, slowly evolving into periodontitis, better known as periodontal disease.
The cause is considered to be a significant increase in the bacterial flora normally present in the dental-gingival sulcus, with the settling of species particularly aggressive. The presence of these specific bacteria generates a secondary inflammatory reaction that causes destruction of the tissues and which, in severe cases, can lead to tooth loss.
The bacterial growth is promoted by poor oral hygiene and concomitant factors such as smoking, diabetes and genetic predisposition. The individual genetic variability is a predisposing factor and / or aggravating periodontal disease. Periodontitis is now considered a potential co-factor in the onset of atherosclerosis with the risk of cardio-vascular and cerebro-vascular diseases. Periodontal disease can be treated on the basis of a correct diagnostic approach which entails, in the objective examination, the use of tests for the analysis of bacterial flora and genetic desposition.
More info:
American Academy of Periodontology
